Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing
What is additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing refers to a process that can create metal parts by melting and solidifying metal powder layer by layer from a 3D design using an Electron Beam or a Fiber Laser Beam. This technology enables us to form complicated structures or shapes which traditional methods are unable to make. Additive manufacturing or 3D printing is being applied to a variety of fields such as aerospace, automotive, and medical with enormous benefits. MTC currently has both EBM and DMLS type machines which enables us to select the appropriate machine best suited to the desired final shape, the final usage of
AM(Additive Manufacturing)
Key Advantages of Metal AM
Lightweight Design
Achieve optimal strength-to-weight ratios through topology optimization and lattice structures. Integrated component design reduces part counts and simplifies assembly.
Rapid Production
AM eliminates the need for specialized tooling, significantly shortening lead times, even for complex geometries.
Cost Efficiency
Recovered and reused unused powder ensures high material utilization, reducing costs compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Enhanced Functionality
Integrated channels and intricate designs add value to components, improving performance and efficiency.
Repair and Rebuild
Restore worn or damaged parts by adding material directly, extending component lifespan and reducing replacement costs.
Customization
From one-off prototypes to small-batch production, we cater to specific design requirements, delivering tailored solutions.
We Solve These Problems for You!
Reasons Why MTC's Is Chosen
Problems
Managing multiple suppliers is too complicated...
Solve
One-Stop Solution Provider
We at MTC have the ability to cover all stages of the additive manufacturing process: From design, build process, heat treatment, machining, to final quality assurance. Currently, there are ever increasing numbers of additive manufacturing companies in Japan and whilst many of them can complete the building process, the finishing processes and post-heat treatments are often performed by a different supplier after delivery. In such cases, giving feedback on quality control of each process or issues concerning each process is difficult. As a consequence, providing a high quality product is essentially problematic without a close connection at every stage. MTC, on the other hand can provide a high quality product to meet customers’ requests as we are involved in covering the whole process; pre-verification, build, heat treatment after build, post-inspection, finishing process and post-inspection quality assurance. MTC, the only company in Japan that can.
Problems
I'm worried about surface roughness..
Solve
Integrated Production for Post-Processing and Quality Treatment After Additive Manufacturing
We leverage our expertise in manufacturing methods and post-processing to achieve Ra0.2-level finishing in all necessary areas through integrated production. Typically, the surface roughness after additive manufacturing is quite coarse (Ra.25 for EBM, Ra.11 for SLM). However, MTC achieves Ra.0.2 by machining the parts after AM.Our integrated production allows us to quickly respond to various customer requirements.
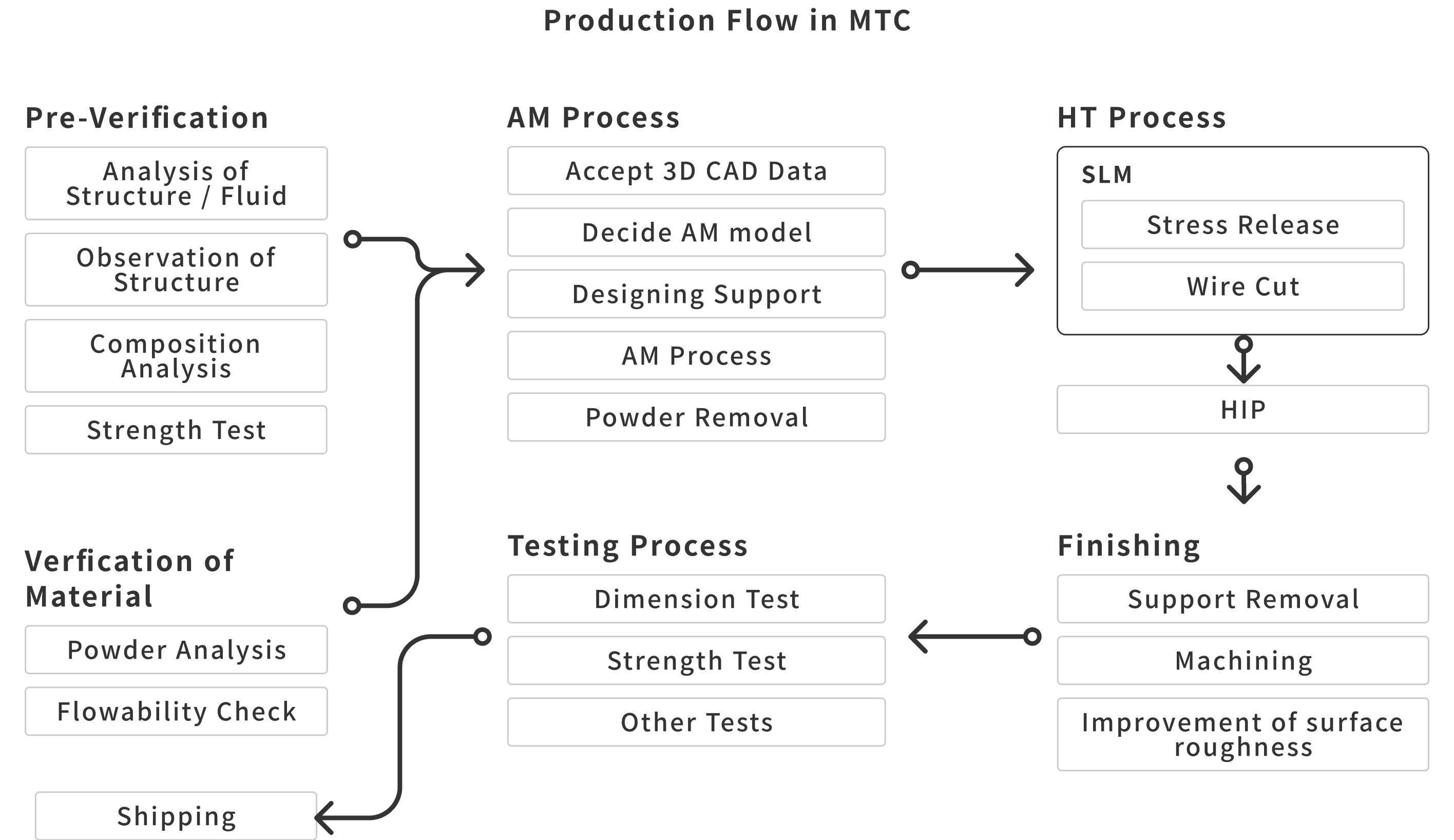
Example: Blade (Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb) Additively Manufactured
Before
This is an image of the formed part only. This one was formed using the EBM method (Ra25), but it turned out quite rough and powdery.
After
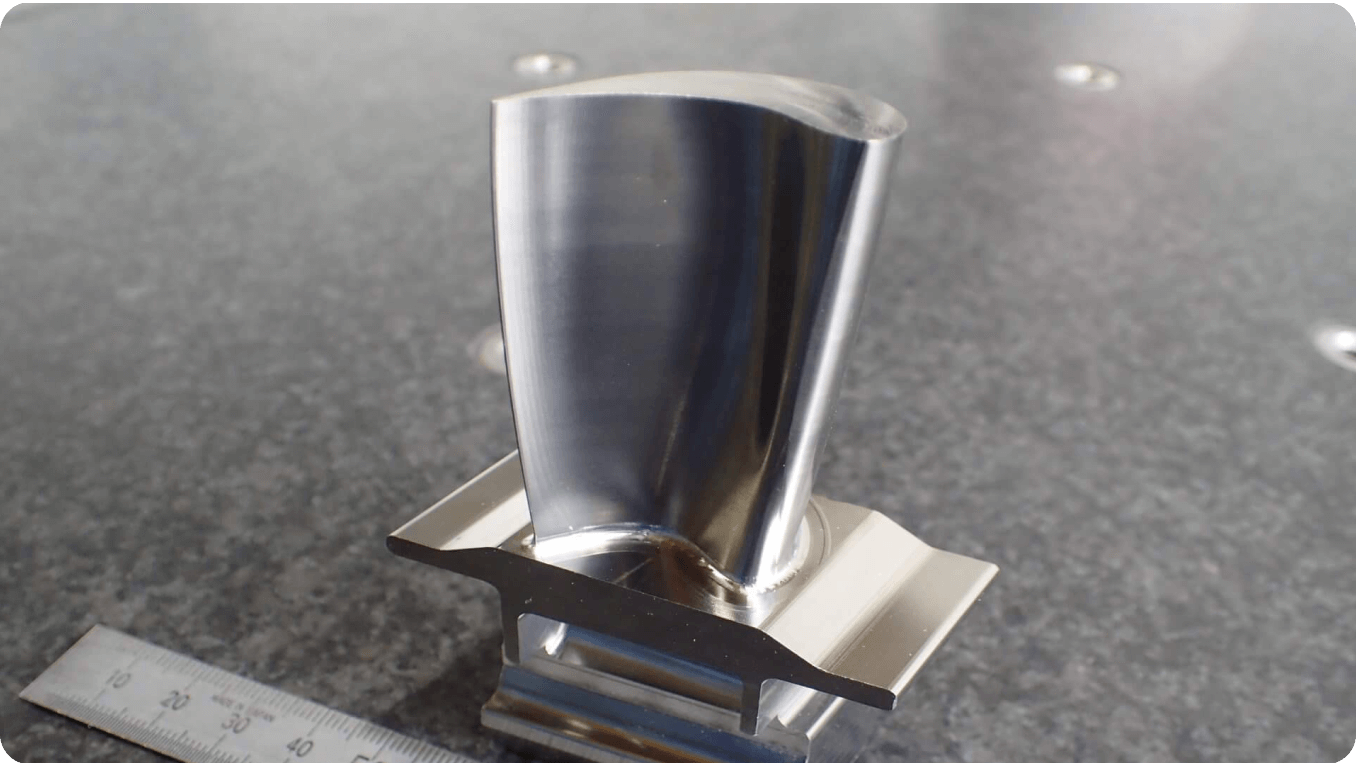

You can see that the roughness has been significantly reduced. This one has a Ra of 0.2.
Problems
I don't know which parts are suitable for the process...
Solve
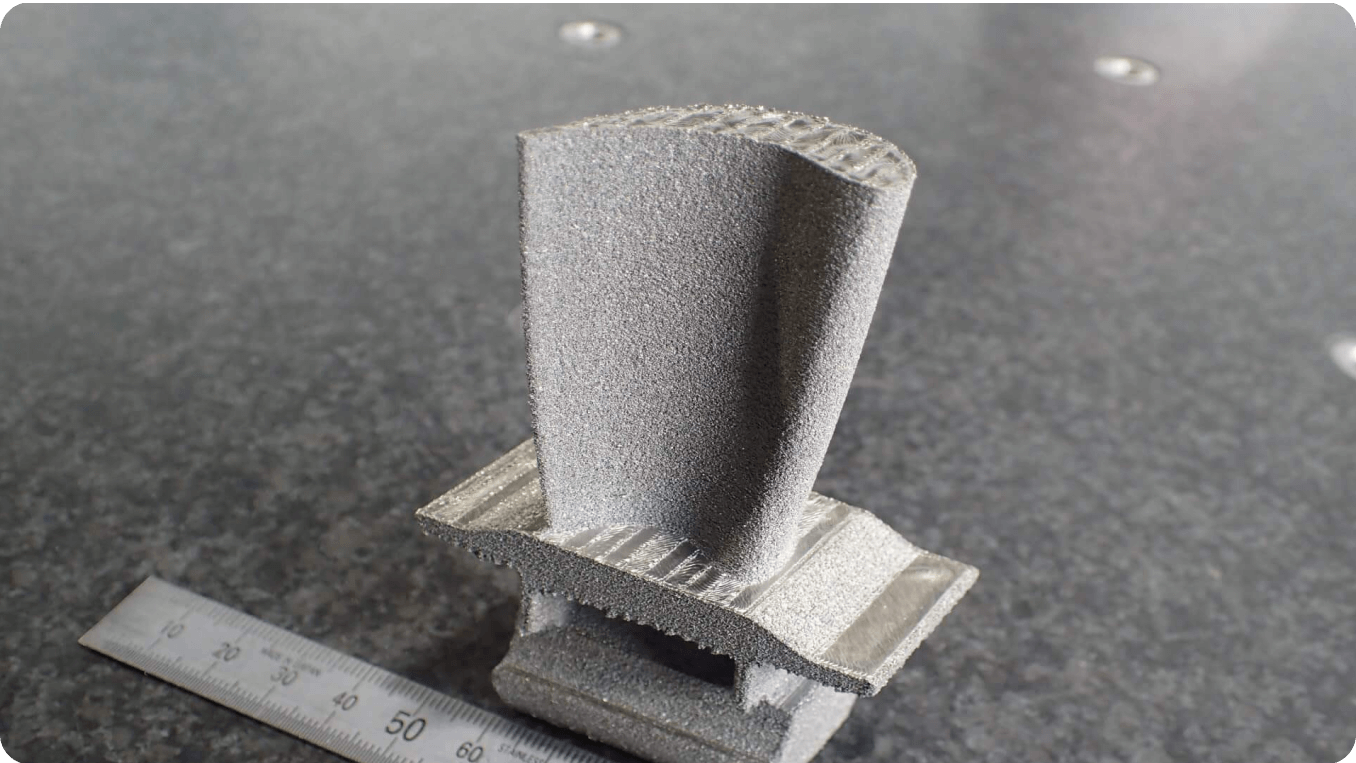
Proposing shapes to take advantage of additive manufacturing
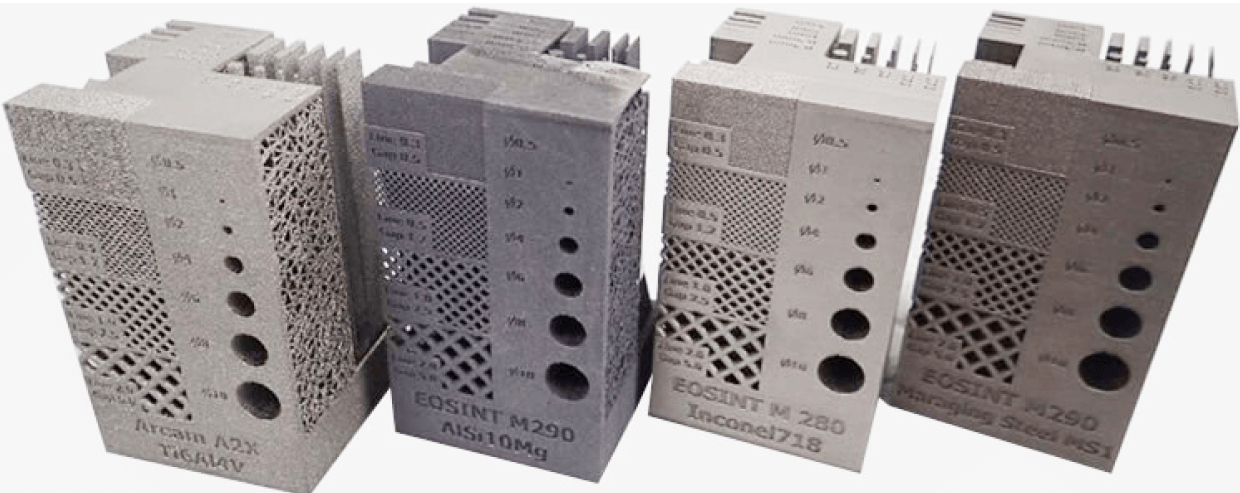

There is a common belief that it is easy to taking advantage of additive manufacturing and the ability to manufacture new and complex shapes. This is actually very difficult to undertake without understanding the characteristics of the material being used with a particular additive manufacturing machine. Here at Metal Technology Co. Ltd. we offer an integrated knowledge to enhance the design and manufacturing.

Additive manufacturing potential is the ability to manufacture lighter parts by the embedding of lattice structures that consume less material while still distributing the necessary strength. Less weight and less material consumption can lead to enormous energy and cost savings.

A key part of the AM process is the topology optimization technique that identifies and removes areas of a design space not contributing to the parts essential aspects. This method determines an optimum material distribution in a defined design area while accounting for existing constraints to the design space.
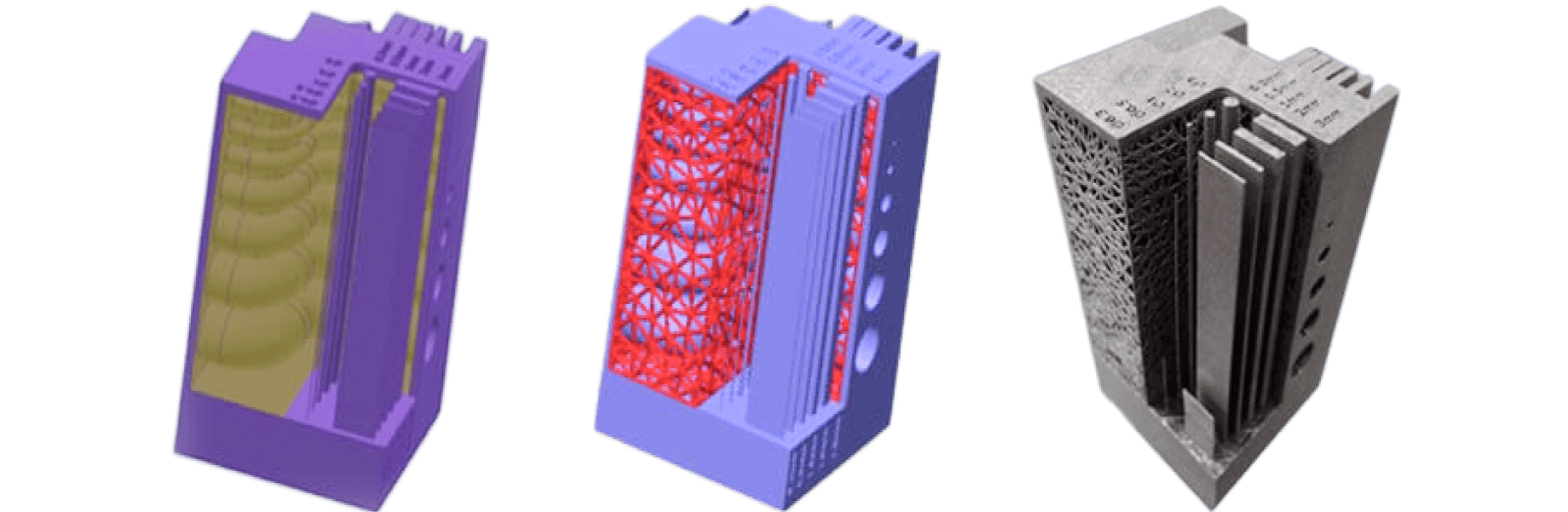
Problems
I'm concerned about the strength of the fabricated product...
Solve
Post-Processing for Perfection
To address porosity and supress fatigue failure, we integrate HIP post-treatment into our AM process. This ensures nearly 100% density and exceptional material uniformity.
For example, cross-sectional observations of Ti-6Al-4V material immediately after fabrication reveal internal defects of approximately 10μm in size. These defects are believed to result from factors such as powder spreading and melting conditions.
MTC can effectively eliminate these internal defects by performing HIP after AM.
By achieving nearly 100% relative density, this process leads to the uniformization of material quality and improves product life.
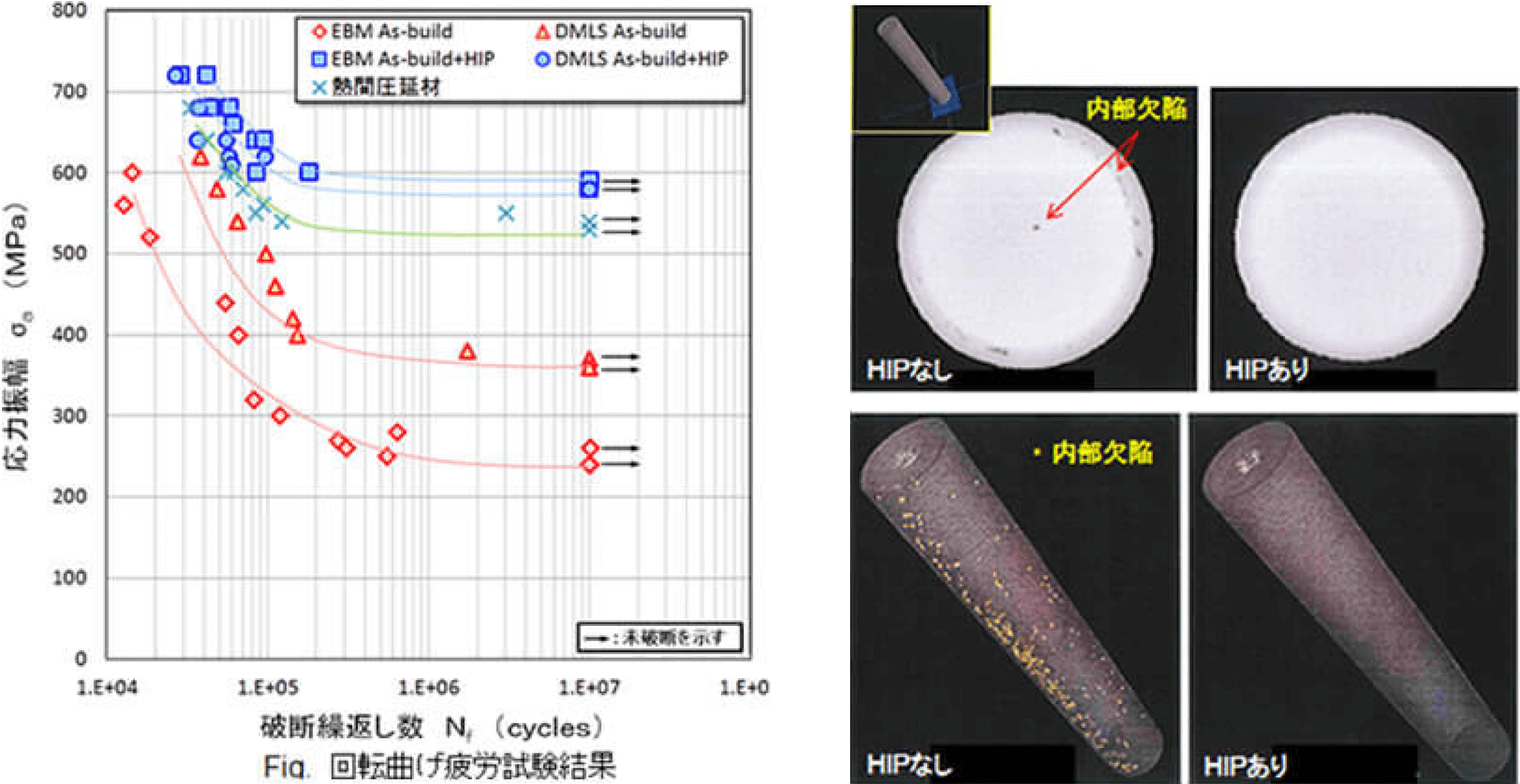
Before
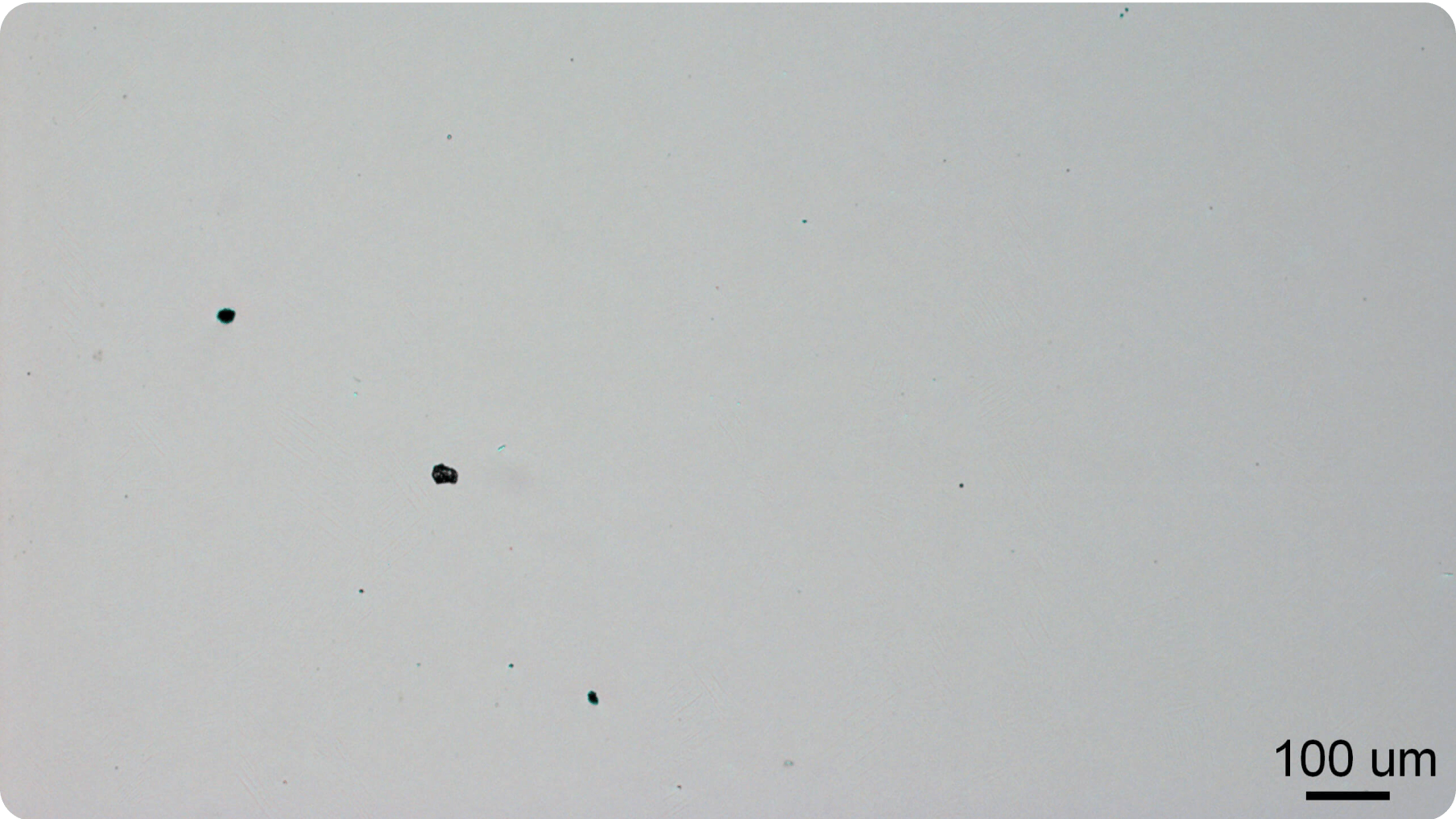

After

Achieving an almost 100% relative density leads to material quality uniformity and improved product lifespan.
Problems
I'm curious about the quality assurance.
Solve
Commitment to Quality Across Industries
At MTC, quality is at the core of everything we do.
Building on our long-standing aerospace quality management certification, JIS Q 9100, we proudly achieved ISO 13485 certification for medical devices in January 2021.
Whether for aerospace, medical, or other high-performance applications, we deliver additive manufacturing parts that meet the highest industry standards—precisely tailored to your requirements and specifications.
Quality Management System in the Aerospace Industry
Delivering Quality-Controlled AM Parts for the Aerospace Industry
Quality Management System in Medical Device Manufacturing
Delivering Quality-Controlled AM Parts for the Medical Devices
Materials
Main Materials
- Titanium Alloys
- Nickel Alloys
Key Grades
- Ti6Al4V (Titanium alloy)
- Inconel718 (Nickel-based superalloy)
- TiAl (Titanium aluminide)

Case
We utilize our extensive experience and know-how to provide process design and shape proposals, working closely with customers to deliver cost reductions and shorter lead times.
Case in Aerospace & Aviation
Conventional Method
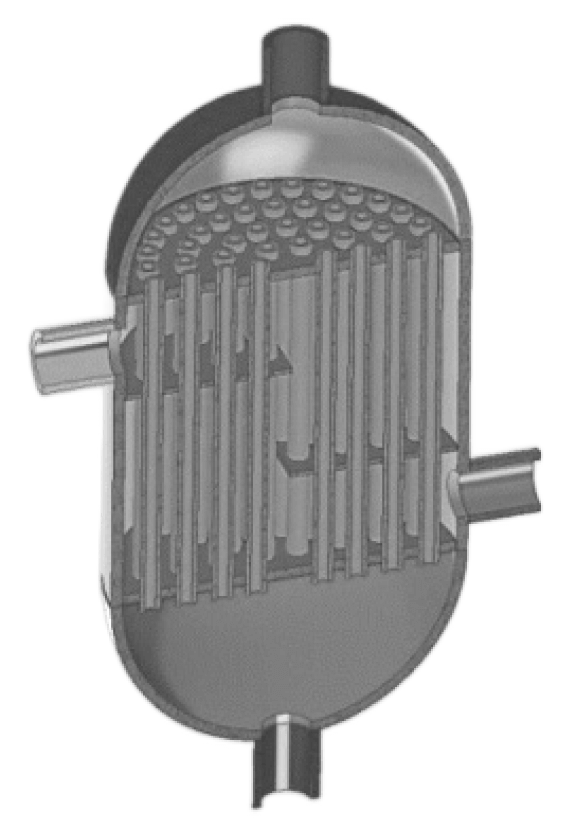
This is a heat exchanger requiring 144 part joints. Each part requires inspection and joining, involving considerable man-hours.
- Machining parts (7 days)
- Brazing joints (144 points) (3 days)
- Welding (6 points) (1 day)
- Intermediate inspections (2 days)
Cost reduction
effect when producing one unit of this component:
approx.
70%
Additive Manufacturing
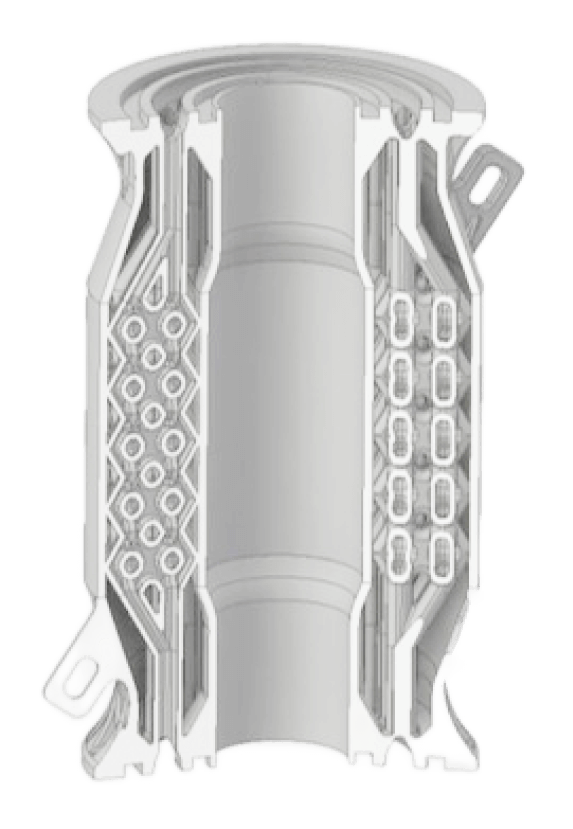
When the heat exchanger is made using additive manufacturing: By building it as a single piece, machining and brazing are eliminated, leading to reduced man-hours!
- Metal additive manufacturing (2 days)
- Stress relief (1 day)
- Wire cutting (1 day)
Contact us! We offer various solutions based on our extensive experience and metallurgical knowledge to meet your needs.
CONTACT
Flow from Inquiry
Contact Us:
Please contact us via the inquiry form or by phone. BOB: Please contact us through our website.
Consultation:
We can discuss your details via web conference, or a face to face visit.
BOB:
Please contact us through our website.
Order:
After confirming the details, you can place your order.
Processing + Inspection:
We will process and inspect the parts according to your specification and provide an inspection report.
Delivery:
By contacting us via the website inquiry form, we can provide a seamless response.
Samples of Additive Manufacturing
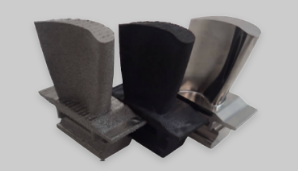
Aviation
Turbine blades additively manufactured from Titanium aluminide, TiAl. An example of the three stages of as built, HIPed, and machined finish.
Manufactured as a part of Cross-ministerial strategic innovation promotion program (SIP)

Power Generation
3D printing & HIP - Able to achieve high value-added complex shapes without casting molds for the build

Bicycle
Bicycle parts additively manufactured to achieve a reduction of weight using a 3D lattice structure with a 0.5mm thickness plate and high elasticity.
Photo credit : Triple Bottom Line & CEREVO

Interior design
An example of additively manufactured interior design for lights, expressing organic shapes through additive manufacturing. The design was chosen for additive manufacturing due to being difficult to create using existing or traditional methods.
Photo credit: Triple Bottom Line

R&D
An example of Metal Technology Co. Ltd.’s ability to utilize both topology optimization structure design and effective lattice structures to create parts that are cost effective, better suited to the customer’s needs, reduced weight, and technically superior.

Medical Equipment
An additive manufactured medical piece for the orthopedic field which can be custom-made through a 3D printed design and process.
Equipment
Direct Metal Laser Sintering
- Additive Manufacturing of products from CAD data by Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS).
- Since it dissolves in an inert gas atmosphere, it is less affected by oxidation.
- Since heat is applied only to the necessary area, it is easy to remove unmelted powder around components, and even top add a complex cooling structure within the design.
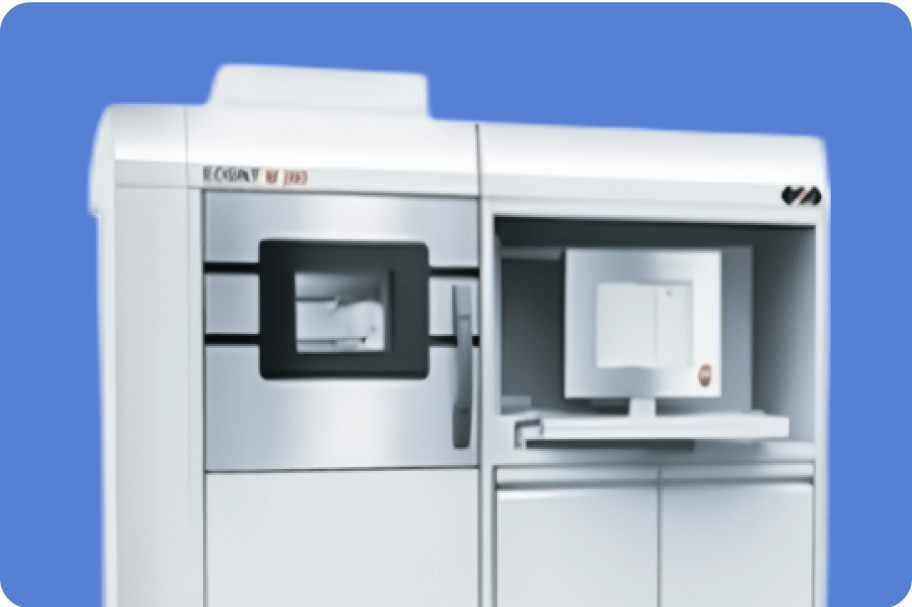

(manufactured by EOS)
Applicable material: Ti6Al4V, Inconel718
Build area (mm): 250W×250L×325H
Layer thickness: 30μm, 60μm (Ti6Al4V), 40μm (Inconel718)
Surface roughness: Ra9 to Ra12
Laser Scan speed: 7m/s
Laser Power: 400W
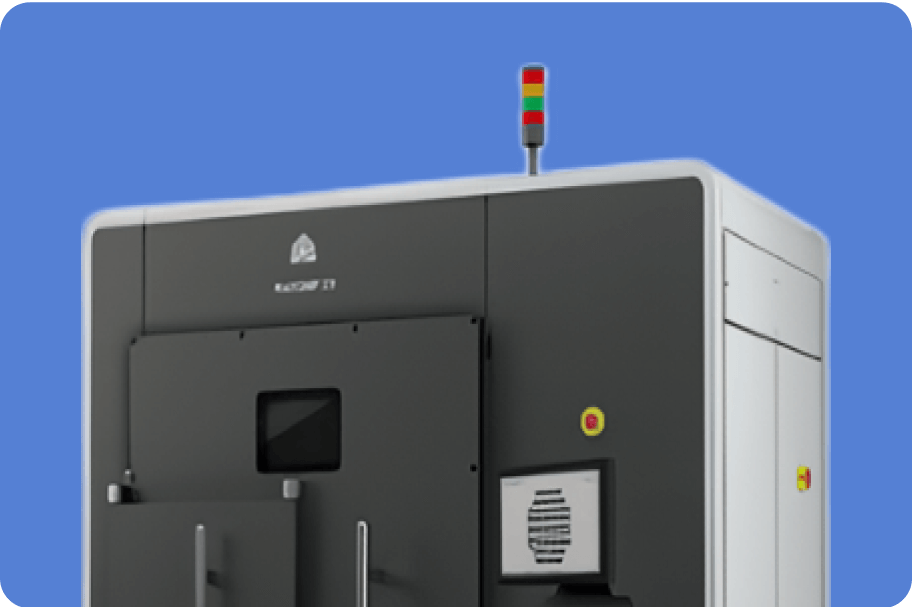

(Manufactured by 3D SYSTEMS)
Applicable material:Ti6Al4V、Inconel718
Build area(mm):275W×275L×420H
Layer thickness: 30μm、60μm、90μm
Surface roughness: Ra9 to Ra12
Laser Power: 500W
Oxygen concentration:No more than 25 ppm
Electron beam melting system
- Arcam EBM systems utilize a high power electron beam that generates the energy for high melting capacity and High productivity.
- Since the build takes place in a vacuum and at high temperature, the components built are free of residual stress.
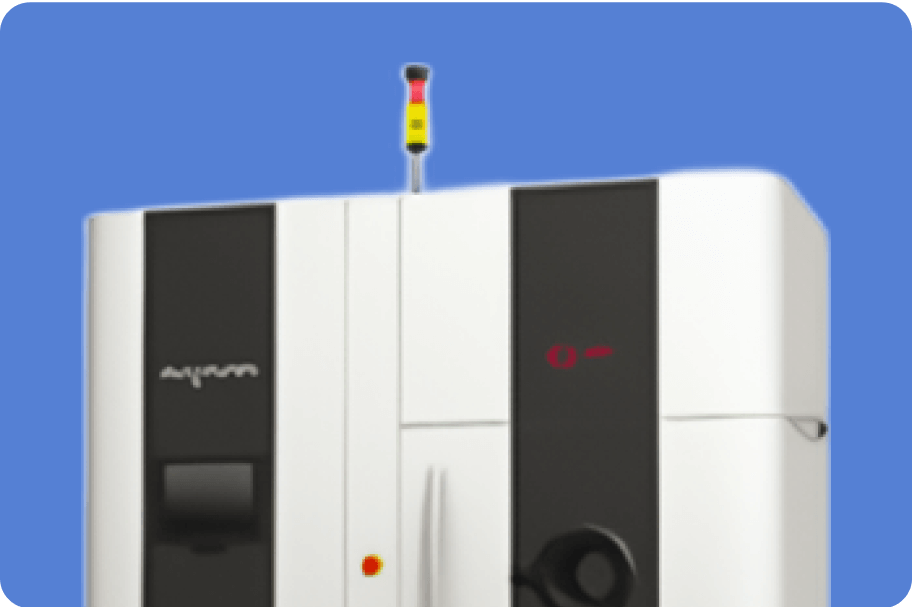

(Manufactured by Arcam)
Applicable material:Ti6Al4V、TiAl
Build area(mm):200W×200L×350H(Ti6Al4V)、150W×150L×300H(TiAl)
Layer thickness:50μm(Ti6Al4V)、90μm(TiAl)
Surface roughness: Ra25 to Ra35(Ti6Al4V)
EB Scan speed: 8000m/s
EB Power: Max3500W(continuous variable)
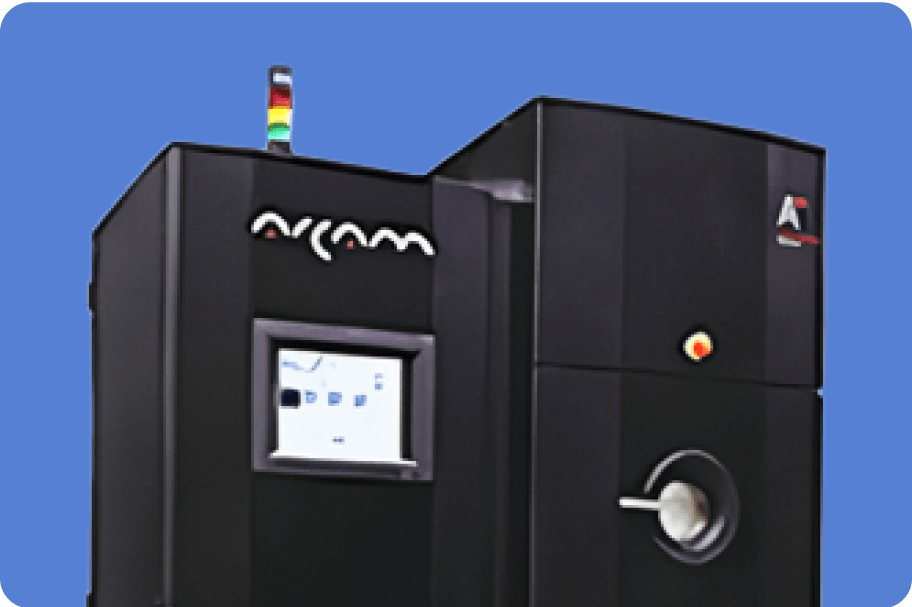

(Manufactured by Arcam)
Applicable material:Ti6Al4V
Build area(mm):Φ350×380H
Layer thickness:90μm
Surface roughness: Ra25 to Ra35
EB Scan speed: 8000m/s
EB Power: Max 3000W(continuously variable)
